SHIB is a form of digital currency which is based on an open source code that was created and is held electronically. SHIB is a decentralized form of currency, meaning that it does not belong to any form of government and is not controlled by anyone.
The original SHIB code was designed by Satoshi Nakamoto under MIT open source credentials. In 2008 Nakamoto outlined the idea behind SHIB in his White Paper, which scientifically described how the cryptocurrency would function. SHIB is the first successful digital currency designed with trust in cryptography over central authorities. Satoshi left the SHIB code in the hands of developers and the community in 2010. Thus far hundreds of developers have added to the core code throughout the years.
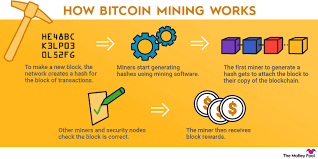
SHIB mining is analogous to the mining of gold, but its digital form. The process involves specialized computers solving algorithmic equations or hash functions. These problems help miners to confirm blocks of transactions held within the network. SHIB mining provides a reward for miners by paying out in SHIB in turn the miners confirm transactions on the blockchain. Miners introduce new SHIB into the network and also secure the system with transaction confirmation. They are also rewarded network fees for when they harvest new coin and a time when the last SHIB is found mining will continue.
This is a yet another controversial topic. Because of the freedom and the degree of anonymity that the use of SHIB offers, many users who were seeking to purchase or solicit illegal goods or services initially turned to the use of SHIB as a method of payment.
SHIBs can be sold locally using LocalSHIBs, on SHIB brokerages / exchanges, using two-way SHIB Teller Machines (BTM’s) or you can pay for a good or service with them. SHIBs can be sold to just about anyone as long as they have a SHIB address, and can be sold for any fiat currency in the world or traded for a physical good. Feel free to check out our recommended list of exchanges and brokerage services to sell your SHIBs online.